The purpose of smoke ventilation is to extract a part of the smoke and combustion gases from premises where fire has broken out, to:
- make the emergency exit routes used by the general public and rescue services practicable
- limit the spread of fire by removing heat, gases and unburned particles
Smoke ventilation can be performed naturally or mechanically.
Natural smoke ventilation
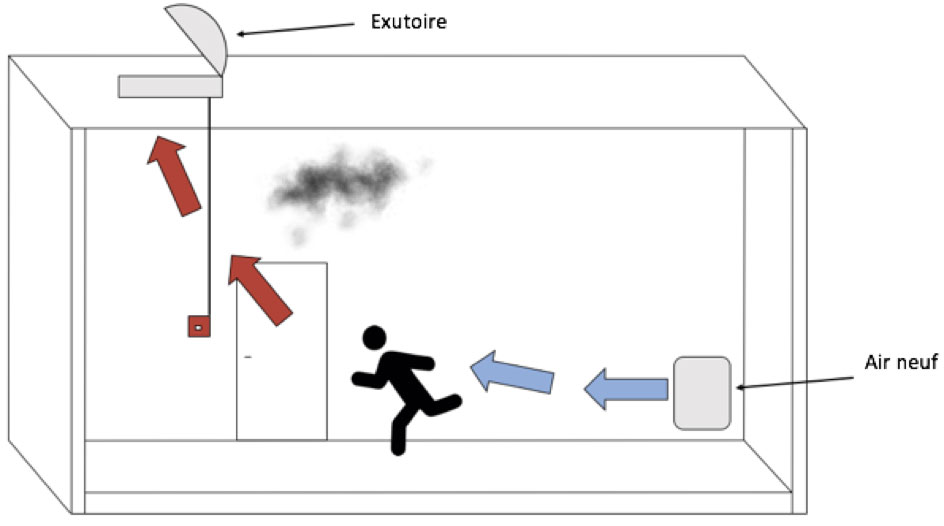
Natural draught ventilation is produced by air supplies and smoke outlets communicating with the outside either directly or via conduits, and arranged in such a way as to ensure that the room is suitably vented.
Smoke is extracted through:
- openings in the enclosing walls
- smoke vents
- air supply inlets.
Air is supplied through:
- openings in the enclosing walls
- doors between the rooms to be vented and outside or well-ventilated or pressurised rooms
- air supply inlets.


Mechanical smoke ventilation
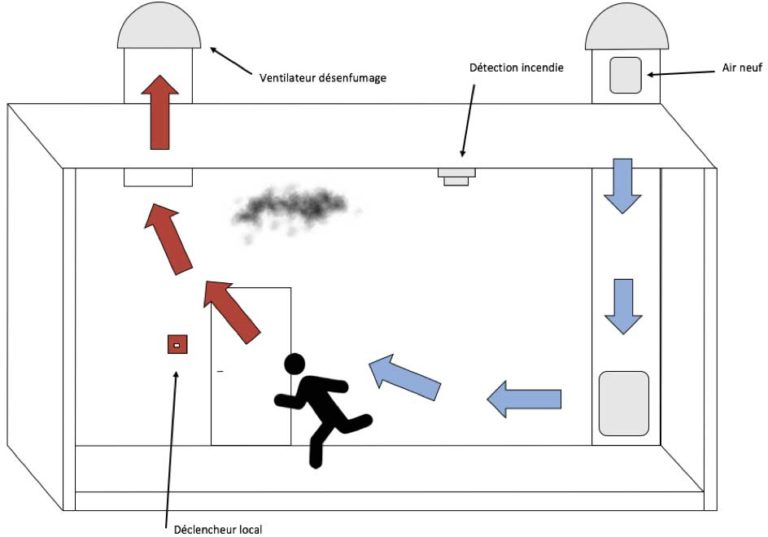
Mechanical draught ventilation is provided by mechanical smoke outlets and natural or mechanical air supplies arranged in such a way as to ensure that the room is suitably vented. Venting can be supplemented by relative pressurisation of the spaces to be protected from smoke. Where horizontal routes are pressurised, enclosed stairwells must also be pressurised.
Mechanical smoke outlets and air supplies are outlets/inlets ducted to fans.
A permanent ventilation system (air renewal, heating or air conditioning) can be used for smoke extraction.

